How Do
Solar Panels
Work?
Solar PV cells are nestled between layers of semi-conducting material, usually silicon. When light shines on them, electrons are knocked loose, and this creates a flow of electricity.
When solar cells are combined they form solar panels, while multiple solar panels connected together form a solar array.
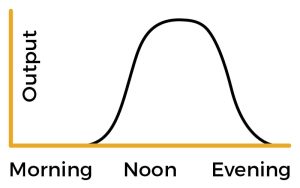
To ensure solar panels are exposed to as much light as possible it is best to have them installed on a south-facing roof, although east- and west-facing roofs are also suitable.
Solar panels should be pitched at an angle of between 10 and 50 degrees, with the optimum angle sitting between 30 and 40 degrees. You should also ensure there are no buildings or trees close by that could leave the panels in shade.
Most solar panels are installed on rooftops, but it is also possible to have them installed on walls or the ground, or to have solar tiles fitted. Be aware, however, that solar tile systems are less cost-effective and typically cost around twice as much as a panel system.
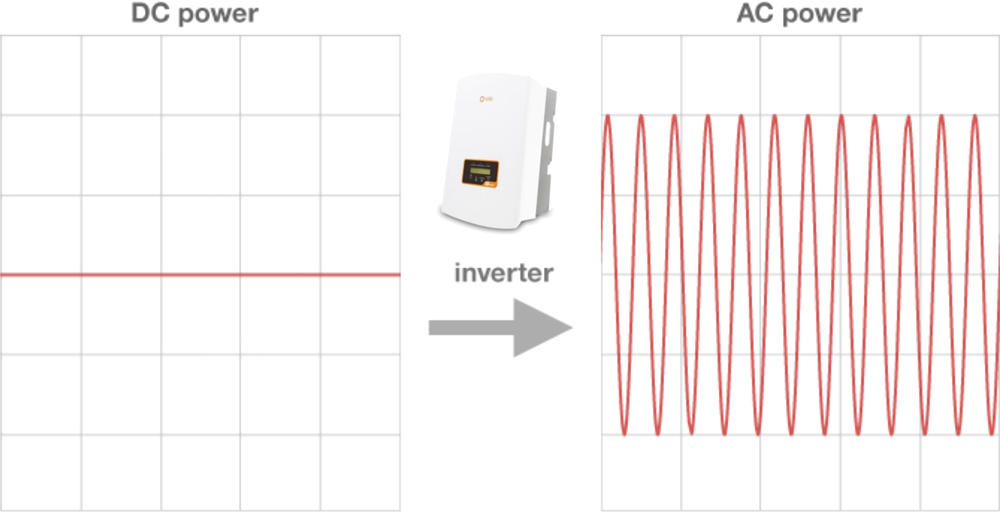
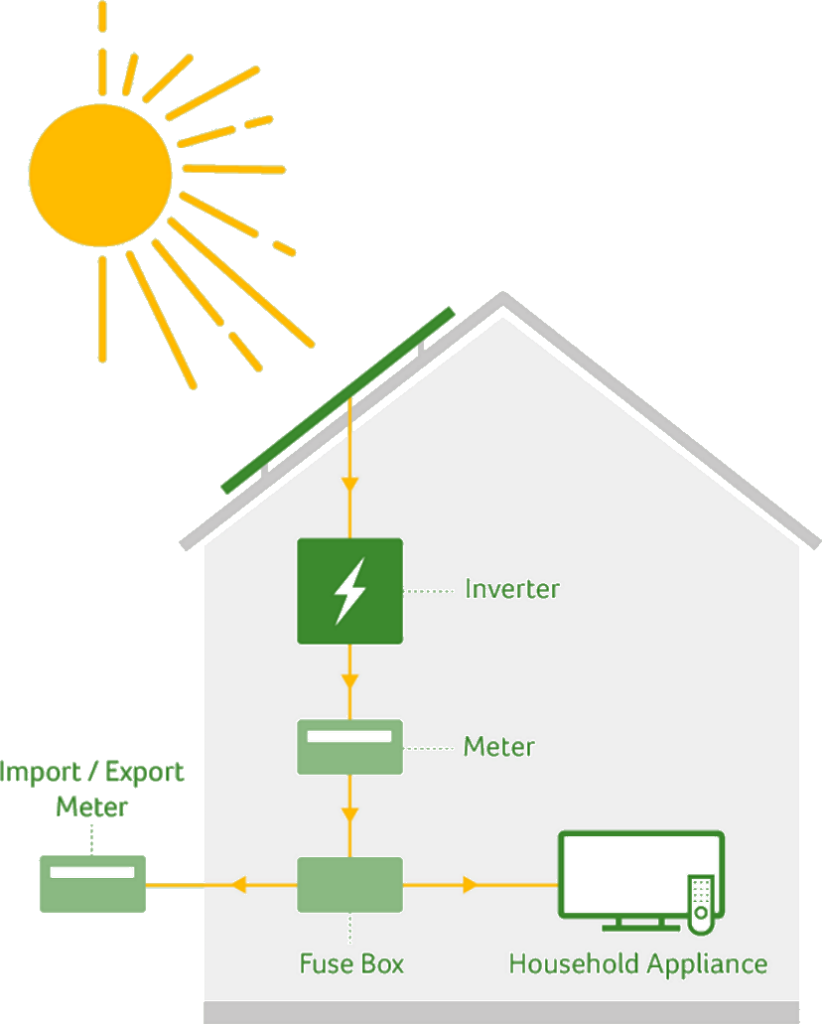
When solar panels are fitted, an inverter will be installed as well to convert the electricity generated from a direct current (DC) to an alternating current (AC), which is used by most home appliances.
How Solar Works

Light from the sun contains many tiny bits of energy called photons.
Some of these photons hit solar modules, which consist of many connected solar cells.
Photons hitting the top layer of a solar cell cause electrons to flow through the bottom layer.
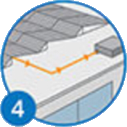
This movement of electrons generates direct current (DC) electricity that flows to an inverter.
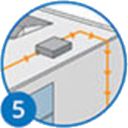
Inverters convert DC electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity.
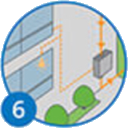
AC electricity is used to power the building, reducing its electricity bills and carbon emissions.
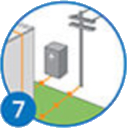
This solar electricity can also charge an energy storage system or flow back into the grid to other buildings.
Solar Panel direction explained for the best results!
North – North-facing solar panel installations should only be considered if none of the above orientations can be achieved.
How an Inverter Works
A vital part of the Solar PV system is the Inverter. A solar inverter works by taking in the variable direct current, or ‘DC’ output, from your solar panels and transforming it into alternating 120V/240V current, or ‘AC’ output.
The appliances in your home run on AC, not DC, which is why the solar inverter must change the DC output that is collected by your solar panels